Every system in the network are prone to cyber attacks. The primary guidelines for protecting them are controlling access to systems. For ensuring effective access controls, segregation of duties or separation of duties(SoD) or toxic combinations is important. The primary objective of the SoD implementation is to prevent fraud and errors.
What is SoD?
Segregation of Duties refers to practices and processes where the knowledge and/or privileges need to complete a process are clearly drawn boundaries. Then the privileges are divided among multiple users so that one user is not having all capabilities.
Principles of SoD
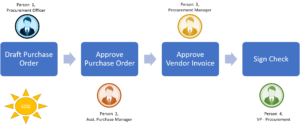
- Sequential Separation – Activity is broken down into steps which are to be performed by different persons (Example: Solicitation, Authorization and implementation of Access rights). This is also referred as two Signature principle. Example cashier in a bank the cheque disbursal requires review signature by accounting clerk and approval signature by branch manager.
- Individual Seperation – When at least two persons must approve an activity before its don
e. Example – Contractor Payment - Spatial Seperation – When different actvities are performed in different locations Example: Locations to receive the stock and storing the material in warehouse
- Factorial Seperation – When several factors contribute to activity completion – Example: Multi factor authentication
Why do we need to adopt SoD ?
* It helps to keep the organization honest with its clients.
* Staff clear with their responsibilities and accountabities in performing the job
* It makes the job duties more transparent and avoids scope for concealment of workflows
* Provides clarity in terms of workflow and helps to identifies blockages
* Minimizes opportunity of Misconduct
* Helps to discover unintentional errors
Its is most required internal controls and an important compliance requirement as per most of the standards such as Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX), GrammLeach-Biley Act (GLBA), ISO 27001 etc., Its very important that no one person should have unlimited access to all the resources. General cyber security example will go with one person have permissions to do both payment request and payment approval and disbursement. The right level of checks and balances is essential.
Lets take a simple scenario of your organization wants to host a website. You are trying to identify the vendor, in this we can understand and evaluate the granularity of controls available with the vendor as a Hosting Service provider.
1. How do you ensure the website storage and control are only accessible my organization ?
2. How are you ensuring that anybody from your organization is not tampering or having access to the content hosted on my account ?
3. Even if they access for maintenance purpose do you have audit log available for us to evaluate ?
4. How long this logs are protected and how can I access them?
5. Can I test these controls before I take the decision on hosting.
Evaluate SoD capabilities of your Identity and Access Management System and relook at policies, procedures to implement the same to minimize the risk.
